What is a Satellite?
What is a Satellite?
• Satellite is a microwave repeater in the space.
• to access a satellite requires „line of sight‟ communication
– the receiver (satellite dish) must be in the satellite‟s „footprint‟
• most satellites are custom built to perform a function.
• Satellite is An artificial body that is projected from earth to orbit either earth (or) another body of solar systems.
Types of satellite
• Information satellites and
• Communication Satellites
Satellite communications
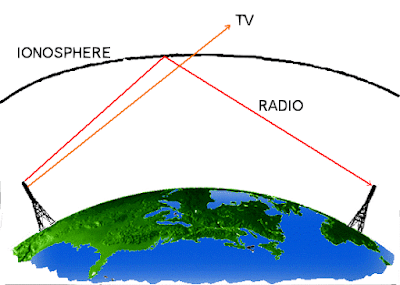
Satellite communications systems exist because earth is a sphere.
– Radio waves travel in straight lines at the microwave frequencies used for wideband communications
– Repeater is needed to convey signals very long distances
Define Satellite Communication.
• It is defined as the use of orbiting satellites to receive, amplify and retransmit data to earth stations.
Satellite-Related Terms
• Earth Stations – antenna systems on or near earth
• Uplink – transmission from an earth station to a satellite
• Downlink – transmission from a satellite to an earth station
• Transponder – electronics in the satellite that convert uplink signals to downlink signals
How does Satellite Communications work?
Generally:
• there is a transmitter on the ground
• the transmitter sends signals to a satellite
– using microwaves
• signal is received & amplified by the satellite
• signal is retransmitted back to Earth
• signal reaches its recipient
– or is ‘bounced back’ to another satellite
Advantages of Satellite Communication
• The coverage area of a satellite greatly exceeds that of a terrestrial system
• can reach remote places
– so people can be contacted wherever they are
• e.g. areas where there is no cellular/fixed line connection
• high bandwidth
– many simultaneous calls can take place
– video & audio can be transmitted in real time
• cost of communication is distance independent
– whether message is sent 10 km or 6000 km
Disadvantages of using Satellite Communication
• are expensive to set up and maintain
• needs line of sight
– can lose signal out of footprint or in built up areas
• affected by weather conditions/interference
– leading to signal degradation
• distance from Earth
– means messages takes time
– can cause unacceptable delay on communications
• general congestion in space
– limitation on number of satellites in geostationary orbit
Service types of satellite
Fixed Service Satellites (FSS)
• Example: Point to Point Communication
Broadcast Service Satellites (BSS)
• Example: Satellite Television/Radio
• Also called Direct Broadcast Service (DBS).
Mobile Service Satellites (MSS)
• Example: Satellite Phones
What are satellites used for?
• television broadcasting
– satellite TV (e.g. Sky)
• telephone communications,
– satellite „phones (e.g. “Iridium”)
• weather forecasting,
– satellite images (visible, infra red, radar)
• Internet communications,
• scientific research,
– climate monitoring, global disaster monitoring, ….
• Global Positioning System
– GPS è satellite navigation („SatNav‟)
– satellite tracking, security
Frequency Bands
• Different kinds of satellites use different frequency bands.
-L–Band: 1 to 2 GHz, used by MSS
-S-Band: 2 to 4 GHz, used by MSS,
-C-Band: 4 to 8 GHz, used by FSS
-X-Band: 8 to 12.5 GHz, used by FSS and in terrestrial imaging, ex: military and meteorological satellites
-Ku-Band: 12.5 to 18 GHz: used by FSS and BSS (DBS)
-K-Band: 18 to 26.5 GHz: used by FSS and BSS
-Ka-Band: 26.5 to 40 GHz: used by FSS
Main satellite orbit type
Geostationary earth orbit (GEO)
• These satellites are in orbit 35,863 km above the earth‟s surface along the equator.
• Objects in Geostationary orbit revolve around the earth at the same speed as the earth rotates. This means GEO satellites remain in the same position relative to the surface of earth.
Advantages
GEO satellite‟s distance from earth gives it a large coverage area, almost a fourth of the earth‟s surface.
-No problem with frequency changes
-GEO satellites have a 24 hour view of a particular area.
-Tracking of the satellite is simplified
-These factors make it ideal for satellite broadcast and other multipoint applications.
Disadvantages
A GEO satellite‟s distance also cause it to have both a comparatively weak signal and a time delay in the signal, which is bad for point to point communication.
-Weak signal after traveling over 35,000 km
-Signal sending delay is substantial
GEO satellites, centered above the equator, have difficulty broadcasting signals to near polar regions
-Polar regions are poorly served
-High transmit power needed and launching of satellites to orbit are complex and expensive.
-Not useful for global coverage for small mobile phones and data transmission
used by TV and weather satellites
– this is why a satellite TV dish is bolted in a fixed position
Broadcasting – mainly TV at present
-DirecTV, PrimeStar, etc.
Point to Multi-point communications
-VSAT, Video distribution for Cable TV
Mobile Services
-Motient (former American Mobile Satellite), INMARSAT, etc.
Medium earth orbit (MEO)
• A MEO satellite is in orbit somewhere between 8,000 km and 18,000 km above the earth‟s surface.
• MEO satellites are similar to LEO satellites in functionality.
• MEO satellites are visible for much longer periods of time than LEO satellites, usually between 2 to 8 hours.
• MEO satellites have a larger coverage area than LEO satellites.
Advantage
-A MEO satellite‟s longer duration of visibility and wider footprint means fewer satellites are needed in a MEO network than a LEO network.
Disadvantage
-A MEO satellite‟s distance gives it a longer time delay and weaker signal than a LEO satellite, though not as bad as a GEO satellite.
GPS by MEO Satellite System
GPS is a medium earth orbit (MEO) satellite system
-GPS satellites broadcast pulse trains with very accurate time signals
-A receiver able to “see” four GPS satellites can calculate its position within 30 m anywhere in world
“You never need be lost again”
– Every automobile and cellular phone will eventually have a GPS location read-out
Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
• LEO satellites are much closer to the earth than GEO satellites, ranging from 500 to 1,500 km above the surface.
• LEO satellites don‟t stay in fixed position relative to the surface, and are only visible for 15 to 20 minutes each pass.
• A network of LEO satellites is necessary for LEO satellites to be useful
Advantages
– A LEO satellite‟s proximity to earth compared to a GEO satellite gives it a better signal strength and less of a time delay, which makes it better for point to point communication.
– A LEO satellite‟s smaller area of coverage is less of a waste of bandwidth.
Disadvantages
– A network of LEO satellites is needed, which can be costly
– LEO satellites have to compensate for Doppler shifts cause by their relative movement.
– Atmospheric drag effects LEO satellites, causing gradual orbital deterioration.
• possible to access satellites from any point on Earth,
– GPS & satellite navigation („Navstar‟)
– use satellite ‘phone in remote locations („Iridium‟ satellites),
– global Internet access.
VSAT
What is a VSAT?
– A very small aperture terminal (VSAT) is a small telecommunication earth station that receives and transmits data, video or voice via satellite.
– The “very small” component of the VSAT acronym refers to the size of the VSAT dish antenna-typically about 60 cm to 3.8 m.
VSAT
• Early Earth Stations in commercial systems were very large and expensive (30 m).
• Need to make system more affordable to end user:
• Increased transmit power from satellite.
• Higher frequencies
• Result: Smaller ES antenna size required.
VSAT SYSTEMS
• Underlying objective of VSAT Systems: bring the service directly to the end-user
• Major reasons for doing this
– Reduce hierarchical distribution network (make more efficient and faster – e.g. Point of Service (POS) credit)
– Reduce distribution costs
VSAT
• Telecommunications and roads are the two major economic growth requirements for developing countries
• Major telecommunications infrastructure does not exist in many developing countries
• SOLUTION
– Distribute links to communities by satellite/VSAT
– Use Wireless Local Loop from the VSAT
Components of VSAT
It has two basic components:
• Ground Segment (earth segment), which is divided into:
– Outdoor Unit (ODU), which contains the antenna.
– Indoor Unit (IDU), which contains the interface between the VSAT and the customer’s Equipment (PCs, TVs, Telephones).
• Space Segment namely satellite.
VSAT frequencies
VSAT uses different frequencies:
• Ku-band frequency: is usually used in North America and Europe by using small VSAT antenna with uplink frequency about 18 GHz and downlink around 12 GHz.
• C-band frequency: is usually used in Asia, Africa and South America and operating with much larger antenna, with uplink frequency around 6 GHz as for downlink frequency around 4 GHz.
• The new Ka-band frequency: is typically in the downlink frequencies up to 22 GHz and uplink frequencies up to 31 GHz.
VSAT Advantages:
– High flexibility to increase the size of the network in the future.
– Able to integrate large number of the networks.
– Cover distant geographical locations.
– Ability to handle Voice, Video and Data.
– Full or partial independence from terrestrial infrastructure
– – Cost savings over terrestrial lines
– Network management from a single point
– Quick deployment,
– Consistent and rapid response time
– Increased network availability and reliability
– Inherent broadcast / multicast platform
VSAT Disadvantages:
– Requires clear line of sight between dish and satellite.
– Outages in some cases, because of the weather. These outages normally last for a few minutes.
What are the benefits of VSAT to the customers?
• Across border – Wide area coverage. Satellite communication offers borderless communication within the satellite coverage area. Reachable to remote areas with digital transmission
• Rapid deployment for new sites – Rapid commissioning of new sites within an existing network
• Cost effective – The pricing is distance independant.
No matter how far your location is, the pricing is still the same.
• Flexibility and efficiency – Network configuration changes such as bandwidth, interfaces, data rates, etc. can be performed remotely from the central network management system.
• Independent of terrestrial infrastructures – Worldwide deregulation of satellite communication services is fast becoming a fact. This allows worldwide implementation of truly private networks.
• Simplicity – quick deployment.
Reliability and Availability – Satellite communication gives 99.7% availability at a BER of 10-7 or even better.
• No local loop issues – VSAT is installed directly on the customer’s site, no terrestrial backhaul costs, inflexibility with increasing bandwidth, terrestrial link availability etc.
VSAT Markets
• Enterprise
– Retail; Oil & Gas; Banking; Government
– POS; Back Office; Browsing; Telemetry
• Telephony
– Public: Public Call Offices, small businesses, farmers, private lines
– Corporate: Telephony/Data infrastructures
• Internet (IP)
– High-speed, always-on, Internet-access for consumers, small businesses and is school
– Intranet and IP infrastructure for the enterprise
– IP multicast-based services
• BTV
• Content delivery