Explanation and examples on classification of computers. ,
Explanation of six types of data processing on basis of process/steps performed. ,
Explanation of seven online services provided by the internet.
1; Classification of computers.
What is Computer
Computer is an electronic device that is designed to work with Information. The term computer is derived from the Latin term ‘computer’, this means to calculate or programmable machine. Computer can not do anything without a Program. It represents the decimal numbers through a string of binary digits. The Word ‘Computer’ usually refers to the Center Processor Unit plus Internal memory.
Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under the control of set of instructions (called program) and gives the result (output) and saves output for the future use. It can process both numerical and non-numerical (arithmetic and logical) calculations.
Digital Computer Definition
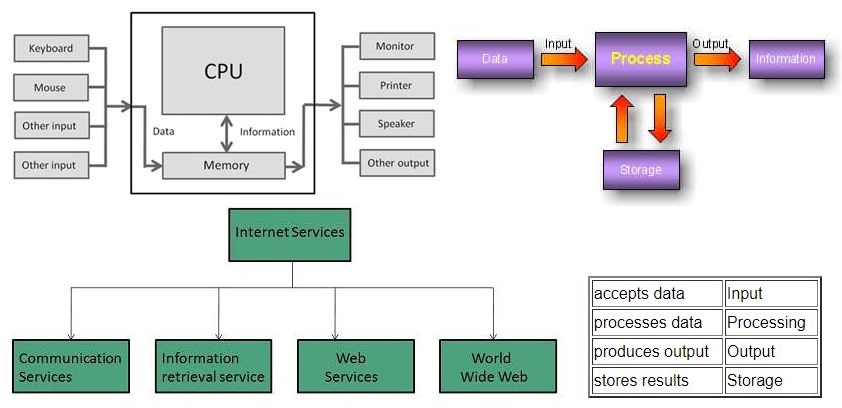
The basic components of a modern digital computer are: Input Device, Output Device, Central Processor Unit (CPU), mass storage device and memory. A Typical modern computer uses LSI Chips. Four Functions about computer are:
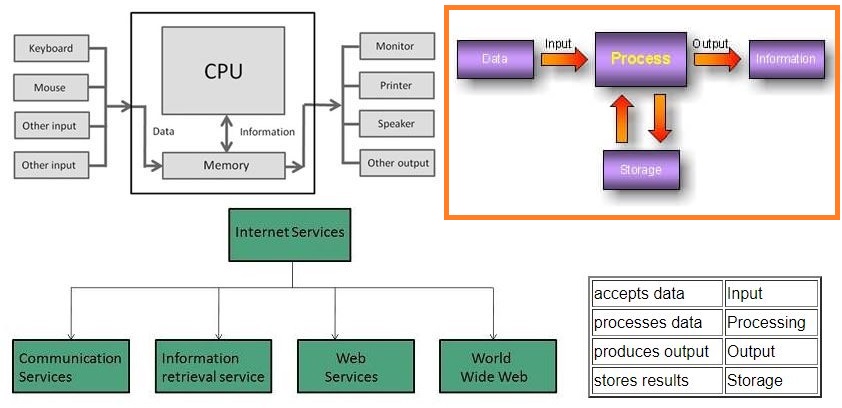
Input (Data):
Input is the raw information entered into a computer from the input devices. It is the collection of letters, numbers, images etc.
Process:
Process is the operation of data as per given instruction. It is totally internal process of the computer system.
Output:
Output is the processed data given by computer after data processing. Output is also called as Result. We can save these results in the storage devices for the future use.
Computer Classification: By Size and Power
Computers differ based on their data processing abilities. They are classified according to purpose, data handling and functionality.
According to functionality, computers are classified as:
• Analog Computer Definition: A computer that represents numbers by some continuously variable physical quantity, whose variations mimic the properties of some system being modeled.
• Personal computer: A personal computer is a computer small and low cost. The term”personal computer” is used to describe desktop computers (desktops).
• Workstation: A terminal or desktop computer in a network. In this context, workstation is just a generic term for a user’s machine (client machine) in contrast to a “server” or “mainframe.”
• Minicomputer: A minicomputer isn’t very mini. At least, not in the way most of us think of mini. You know how big your personal computer is and its related family.
• Mainframe: It refers to the kind of large computer that runs an entire corporation.
• Supercomputer: It is the biggest, fastest, and most expensive computers on earth.
• Microcomputer: Your personal computer is a microcomputer.
According to purpose, computers are either general purpose or specific purpose. General purpose computers are designed to perform a range of tasks. They have the ability to store numerous programs, but lack in speed and efficiency. Specific purpose computers are designed to handle a specific problem or to perform a specific task. A set of instructions is built into the machine.
According to data handling, computers are analog, digital or hybrid. Analog computers work on the principle of measuring, in which the measurements obtained are translated into data. Modern analog computers usually employ electrical parameters, such as voltages, resistances or currents, to represent the quantities being manipulated. Such computers do not deal directly with the numbers. They measure continuous physical magnitudes. Digital computers are those that operate with information, numerical or otherwise, represented in a digital form. Such computers process data into a digital value (in 0s and 1s). They give the results with more accuracy and at a faster rate. Hybrid computers incorporate the measuring feature of an analog computer and counting feature of a digital computer. For computational purposes, these computers use analog components and for storage, digital memories are used.
According to functionality, Type of computers are classified as :
Analog Computer
An analog computer (spelt analogue in British English) is a form of computer that uses continuous physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved.
Digital Computer
A computer that performs calculations and logical operations with quantities represented as digits, usually in the binary number system
Hybrid Computer (Analog + Digital)
A combination of computers those are capable of inputting and outputting in both digital and analog signals. A hybrid computer system setup offers a cost effective method of performing complex simulations.
On the basis of Size: Type of Computer
Super Computer
The fastest and most powerful type of computer Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications that require immense amounts of mathematical calculations. For example, weather forecasting requires a supercomputer. Other uses of supercomputers include animated graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, and petroleum exploration.
The chief difference between a supercomputer and a mainframe is that a supercomputer channels all its power into executing a few programs as fast as possible, whereas a mainframe uses its power to execute many programs concurrently.
Mainframe Computer
A very large and expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds, or even thousands, of users simultaneously. In the hierarchy that starts with a simple microprocessor (in watches, for example) at the bottom and moves to supercomputers at the top, mainframes are just below supercomputers. In some ways, mainframes are more powerful than supercomputers because they support more simultaneous programs. But supercomputers can execute a single program faster than a mainframe.
Mini Computer
A mid-sized computer. In size and power, minicomputers lie between workstations and mainframes. In the past decade, the distinction between large minicomputers and small mainframes has blurred, however, as has the distinction between small minicomputers and workstations. But in general, a minicomputer is a multiprocessing system capable of supporting from 4 to about 200 users simultaneously.
Micro Computer or Personal Computer
• Desktop Computer: a personal or micro-mini computer sufficient to fit on a desk.
• Laptop Computer: a portable computer complete with an integrated screen and keyboard. It is generally smaller in size than a desktop computer and larger than a notebook computer.
• Palmtop Computer/Digital Diary /Notebook /PDAs: a hand-sized computer. Palmtops have no keyboard but the screen serves both as an input and output device.
Workstations
A terminal or desktop computer in a network. In this context, workstation is just a generic term for a user’s machine (client machine) in contrast to a “server” or “mainframe.”
2; Types of data processing on basis of process/steps performed.
Data processing
Various data processing methods are used to converts raw data to meaningful information through a process. Data is manipulated to produce results that lead to a resolution of a problem or improvement of an existing situation. Similar to a production process, it follows a cycle where inputs (raw data) are fed to a process (computer systems, software, etc.) to produce output (information and insights).
Methods of Data Processing and Data Processing Techniques
There are number of methods and types of data processing. Based on the data processing system and the requirement of the project, suitable data processing methods can be used. Three methods of data processing have been presented below:
l Manual Data Processing
l Mechanical Data Processing
l Electronic Data Processing
Manual Data Processing
Data is processed manually without using any machine or tool to get the required results. In manual data processing, all the calculations and logical operations are performed manually on the data. Similarly, data is transferred manually from one place to another. This method of data processing is very slow, and errors may occur in the output. Mostly, is processed manually in many small business firms as well as government offices & institutions. In an educational institute, for example, marks sheets, fee receipts, and other financial calculations (or transactions) are performed by hand. This method is avoided as far as possible because of the very high probability of error, labor intensive and very time-consuming. This type of data processing forms the very primitive stage when technology was not available, or it was not affordable. With the advancement of technology, the dependency on manual methods has drastically decreased. This also makes processing expensive and requires large manpower depending on the data required to be processed. Example includes selling of commodity on shop.
Mechanical Data Processing
In this method, data is processed by using different devices like typewriters, mechanical printers or other mechanical devices. This method of data processing is faster and more accurate than manual data processing. These are faster than the manual mode but still forms the early stages of data processing. With invention and evolution of more complex machines with better computing power this type of processing also started fading away. Examination boards and printing press use mechanical data processing devices frequently. Any device which facilitates data processing can be considered under this category. The output from this method is still very limited.
Electronic Data Processing (EDP)
This is a modern technique to process data. The data is processed through a computer; Data and set of instructions are given to the computer as input, and the computer automatically processes the data according to the given set of instructions. The computer is also known as electronic data processing machine. Electronic Data Processing is the fastest and best available method with highest reliability and accuracy. Technology used is latest as this method uses computers. Manpower required is minimal. Processing can be done through various programs and predefined set of rules. Processing of large amount of data with high accuracy is almost impossible which makes it best among the available types of data processing. For example, in a computerized education environment results of students are prepared through a computer; in banks, accounts of customers are maintained (or processed) through computers.
Types of data processing on basis of process/steps performed
There are number of methods and techniques which can be adopted for processing of data depending upon the requirements, time availability, software and hardware capability of the technology being used for data processing. There are number of types of data processing methods.
l Batch Processing
l Real time processing
l Online Processing
l Distributed Processing
l Multiprocessing
l Time sharing
Batch Processing
This is one of the widely used type of data processing which is also known as serial/sequential, tacked/queued of offline processing. The fundamental of this type of processing is the that different jobs of different users are processed in the order received. Once the stacking of jobs is complete they are provided/sent for processing while maintaining the same order. This processing of a large volume of data helps in reducing the processing cost thus making it data processing economical.
Batch Processing is a method where the information to be organized is sorted into groups to allow for efficient and sequential processing. Online Processing is a method that utilizes Internet connections and equipment directly attached to a computer. It is used mainly for information recording and research. Real-Time Processing is a technique that can respond almost immediately to various signals to acquire and process information. Distributed Processing is commonly utilized by remote workstations connected to one big central workstation or server. ATMs are good examples of this data processing method. Examples include: Examination, payroll and billing system.
Online Processing
This processing method is a part of automatic processing method. This method at times known as direct or random access processing. Under this method the job received by the system is processed at same time of receiving. This can be considered and often mixed with real-time processing. This system features random and rapid input of transaction and user defined/ demanded direct access to databases/content when needed.
This is a method that utilizes Internet connections and equipment directly attached to a computer. This allows for the data stored in one place and being used at an altogether different place. Cloud computing can be considered as an example which uses this type of processing. It is used mainly for information recording and research.
Real-Time Processing
As the name suggests this method is used for carrying out real-time processing. This is required where the results are displayed immediately or in lowest time possible. The data fed to the software is used almost instantaneously for processing purpose. The nature of processing of this type of data processing requires use of internet connection and data is stored/used online. No lag is expected/acceptable in this type and receiving and processing of transaction is carried out simultaneously. This method is costly than batch processing as the hardware and software capabilities are better. Example includes banking system, tickets booking for flights, trains, movie tickets, rental agencies etc.
This technique can respond almost immediately to various signals to acquire and process information. These involve high maintenance and upfront cost attributed to very advanced technology and computing power. Time saved is maximum in this case as the output is seen in real time. For example in banking transactions.
Distributed Processing
This method is commonly utilized by remote workstations connected to one big central workstation or server. ATMs are good examples of this data processing method. All the end machines run on a fixed software located at a particular place and make use of exactly same information and sets of instruction.
Multi Processing
This type of processing perhaps the most widely used types of data processing. It is used almost everywhere and forms the basic of all computing devices relying on processors. Multi processing makes use of CPUs (more than one CPU). The task or sets of operations are divided between CPUs available simultaneously thus increasing efficiency and throughput. The break down of jobs which needs be performed are sent to different CPUs working parallel within the mainframe. The result and benefit of this type of processing is the reduction in time required and increasing the output . Moreover CPUs work independently as they are not dependent on other CPU, failure of one CPU does not result in halting the complete process as the other CPUs continue to work. Examples include processing of data and instructions in computer, laptops, mobile phones
Time sharing
Time based used of CPU is the core of this data processing type. The single CPU is used by multiple users. All users share same CPU but the time allocated to all users might differ. The processing takes place at different intervals for different users as per allocated time. Since multiple users can uses this type it is also referred as multi access system. This is done by providing a terminal for their link to main CPU and the time available is calculated by dividing the CPU time between all the available users as scheduled.
Data Processing Cycle
The Data Processing Cycle is a series of steps carried out to extract information from raw data. Although each step must be taken in order, the order is cyclic. The output and storage stage can lead to the repeat of the data collection stage, resulting in another cycle of data processing. The cycle provides a view on how the data travels and transforms from collection to interpretation, and ultimately, used in effective business decisions. There are 6 stages of data processing cycle:
l Collection
l Preparation
l Input
l Processing
l Output & Interpretation
l Storage
Data Processing System
It system is a combination of machines and people that for a set of inputs produces a defined set of outputs. The inputs and outputs are interpreted as data, facts, information, depending on the interpreter’s relation to the system.
A system may involve some combination of:
l Conversion is converting data to another format.
l Validation – Ensuring that supplied data is “clean, correct and useful.”
l Sorting – “arranging items in some sequence and/or in different sets.”
l Summarization – reducing detail data to its main points.
l Aggregation – combining multiple pieces of data.
l Analysis – the “collection, organization, analysis, interpretation and presentation of data.”.
l Reporting – list detail or summary data or computed information.
l Presentation – data presentation is helpful in taking decisions
Applications
Commercial Data Processing
Commercial data processing involves a large volume of input data, relatively few computational operations, and a large volume of output. For example, an insurance company needs to keep records on tens or hundreds of thousands of policies, print and mail bills, and receive and post payments.
Data Analysis
In a science or engineering field, the terms data processing and information systems are considered too broad, and the more specialized term data analysis is typically used. Data analysis makes use of specialized and highly accurate algorithms and statistical calculations that are less often observed in the typical general business environment.
3; Seven online services provided by the internet.
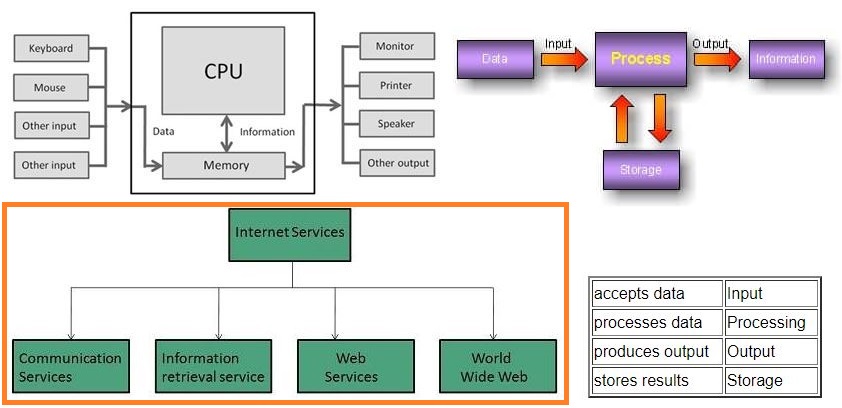
Internet Services allows us to access huge amount of information such as text, graphics, sound and software over the internet. Following diagram shows the four different categories of Internet Services.
Communication Services
There are various Communication Services available that offer exchange of information with individuals or groups. The following table gives a brief introduction to these services:
|
S.N.
|
Service Description
|
|
1
|
Electronic Mail
Used to send electronic message over the internet. |
|
2
|
Telnet
Used to log on to a remote computer that is attached to internet. |
|
3
|
Newsgroup
Offers a forum for people to discuss topics of common interests. |
|
4
|
Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
Allows the people from all over the world to communicate in real time. |
|
5
|
Mailing Lists
Used to organize group of internet users to share common information through e-mail. |
|
6
|
Internet Telephony (VoIP)
Allows the internet users to talk across internet to any PC equipped to receive the call. |
|
7
|
Instant Messaging
Offers real time chat between individuals and group of people. Eg. Yahoo messenger, MSN messenger. |
Information Retrieval Services
There exist several Information retrieval services offering easy access to information present on the internet. The following table gives a brief introduction to these services:
|
S.N.
|
Service Description
|
|
1
|
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Enable the users to transfer files. |
|
2
|
Archie
It’s updated database of public FTP sites and their content. It helps to search a file by its name. |
|
3
|
Gopher
Used to search, retrieve, and display documents on remote sites. |
|
4
|
Very Easy Rodent Oriented Netwide Index to Computer Achieved (VERONICA)
VERONICA is gopher based resource. It allows access to the information resource stored on gopher’s servers. |
Web Services
Web services allow exchange of information between applications on the web. Using web services, applications can easily interact with each other.
The web services are offered using concept of Utility Computing.
World Wide Web (WWW)
WWW is also known as W3. It offers a way to access documents spread over the several servers over the internet. These documents may contain texts, graphics, audio, video, hyperlinks. The hyperlinks allow the users to navigate between the documents
As we live in an age where we tend to be very dependent on phones, computers, and other devices. The advantage of this lies in the fact that one can easily find out if a husband or wife is having affairs by gaining access to their phones. Good pro, tomcyberghost@gmail.com does great with such tasks and you attain remote access to monitor device activities, A to Z. Phone calls, text messages, call logs, live call recording, location, media files, and more. This prõś service works perfectly well for all device types. Text & Calls +1 (404) 941-6785