GSM, HSDPA, LTE 4G. Digital Mobile Network Technologies
GSM (Global System for Mobile communication)
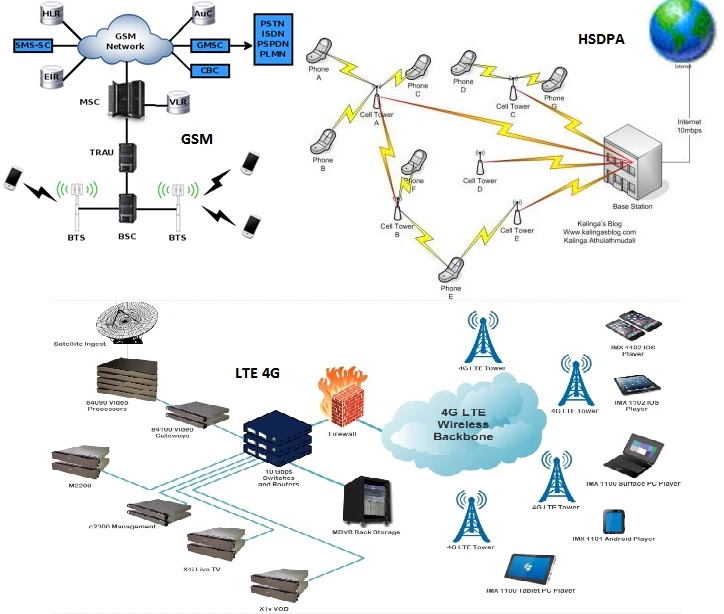
GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) is a digital mobile network that is widely used by mobile phone users in Europe and other parts of the world. GSM uses a variation of time division multiple access (TDMA) and is the most widely used of the three digital wireless telephony technologies: TDMA, GSM and code-division multiple access (CDMA). GSM digitizes and compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot. It operates at either the 900 megahertz (MHz) or 1,800 MHz frequency band.
GSM, together with other technologies, is part of the evolution of wireless mobile telecommunications that includes High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE) and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS).
Composition of the network
The GSM network has four separate parts that work together to function as a whole: the mobile device itself, the base station subsystem (BSS), the network switching subsystem (NSS) and the operation and support subsystem (OSS).
The mobile device connects to the network via hardware. The subscriber identity module (SIM) card provides the network with identifying information about the mobile user.
The BSS handles traffic between the cell phone and the NSS. It consists of two main components: the base transceiver station (BTS) and the base station controller (BSC). The BTS contains the equipment that communicates with the mobile phones, largely the radio transmitter receivers and antennas, while the BSC, is the intelligence behind it. The BSC communicates with and controls a group of base transceiver stations.
The NSS portion of the GSM network architecture, often called the core network, tracks the location of callers to enable the delivery of cellular services. Mobile carriers own the NSS. The NSS has a variety of parts, including mobile switching center (MSC) and home location register (HLN). These components perform different functions, such as routing calls and Short Message Service (SMS) and authenticating and storing caller account information via SIM cards.
HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access)
HSDPA, short for High-Speed Downlink Packet Access, is a new protocol for mobile telephone data transmission. It is known as a 3.5G (G stands for generation) technology. Essentially, the standard will provide download speeds on a mobile phone equivalent to an ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) line in a home, removing any limitations placed on the use of your phone by a slow connection. It is an evolution and improvement on W-CDMA, or Wideband Code Division Multiple Access, a 3G protocol. This protocol improves the data transfer rate by a factor of at least five over W-CDMA. HSDPA can achieve theoretical data transmission speeds of 8-10 Mbps (megabits per second). Though any data can be transmitted, applications with high data demands such as video and streaming music are the focus of HSDPA.
HSDPA improves on W-CDMA by using different techniques for modulation and coding. It creates a new channel within W-CDMA called HS-DSCH, or high-speed downlink shared channel. That channel performs differently than other channels and allows for faster downlink speeds. It is important to note that the channel is only used for downlink. That means that data is sent from the source to the phone. It isn’t possible to send data from the phone to a source using HSDPA. The channel is shared between all users which lets the radio signals to be used most effectively for the fastest downloads.
The widespread availability of this protocol may take a while to be realized, or it may never be achieved. Most countries did not have a widespread 3G network in place as of the end of 2005. Many mobile telecommunications providers are working quickly to deploy 3G networks which can be upgraded to 3.5G when the market demand exists. Other providers tested HSDPA through 2005 and are rolling out the service in mid to late 2006. Early deployments of the service will be at speeds much lower than the theoretically possible rates. Early service will be at 1.8 Mbps, with upgrades to 3.6Mbps as devices are made available that can handle that increased speed.
The long-term acceptance and success of the protocol is unclear, because it is not the only alternative for high speed data transmission. Standards like CDMA2000 1xEV-DO and WiMax are other potential high speed standards. Since HSDPA is an extension of W-CDMA, it is unlikely to succeed in locations where W-CDMA has not been deployed. Therefore, the eventual success of the protocol as a 3.5G standard will first depend upon the success of W-CDMA as a 3G standard.
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
LTE is an abbreviation for Long Term Evolution. LTE is a 4G wireless communications standard developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) that’s designed to provide up to 10x the speeds of 3G networks for mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, netbooks, notebooks and wireless hotspots.
4G Technology and Networks
4G technologies are designed to provide IP-based voice, data and multimedia streaming at speeds of at least 100 Mbit per second and up to as fast as 1 GBit per second.
4G LTE is one of several competing 4G standards along with Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB) and WiMax (IEEE 802.16). The leading cellular providers have started to deploy 4G technologies, with Verizon and AT&T launching 4G LTE networks and Sprint utilizing its new 4G WiMax network. In terms of mobile devices, many newer Android-based smartphones are 4G LTE capable, and both the iPhone 5 and the iPad 3 are expected to have built-in 4G LTE capabilities when released in the second half of 2012.
Global LTE Speeds
In November 2016, OpenSignal’s The State of LTE report indicates than while LTE continues to expand and see strength, globally, download speeds average 17.4 Mbps but speeds approach 50 Mbps in the most advanced 4G countries.
I am constantly thought about this, thank you for putting up. cellphone pos
This is an amazing blog; I was trying to figure out how to keep in contact with your blog until I find out a decent iphone app for reading wordpress blogs. I really wish you to have a good day and keep with the good work! social spy whatsapp
Very interesting points you have observed , regards for putting up. grouphowto
I just have to introduce this hacker that I have been working with him on getting my credit score been boosted across the Equifax, TransUnion and Experian report. He made a lot of good changes on my credit report by erasing all the past eviction, bad collections and DUI off my credit report history and also increased my FICO score above 876 across my three credit bureaus report you can contact him for all kind of hacks . Email him here support@wavedrive.tech go on their website wavedrive.tech for more details,Whatsapp No:+14106350697 if you want to chat them up,One thing i can assure you would not regret this at all he is 100% legit.
Hey everyone, I don't really know much about this hacking thing's but I can direct you to a professional hacking company who helped me to track and hack my girlfriend's iPhone and his Facebook respectively.. If you need to check on your partner's sincerity, employee's honesty, recover your email passwords, Social networks (i.e. Facebook, Twitter, IG), change your school grades, clear your criminal records, gain access to bank accounts,spy on phone. you can just contact them at. Their charges are minimal and negotiable contact them at TOMCYBERGHOST@GMAIL.COM tell him you are from me.